Matchmoving allows us to place 3D objects into a 2D sequence and lock them in place, even when the camera moves.
So how does this happen? The process of matchmoving recreates the original camera path (position) and the direction the camera is pointing (rotation).
What else does matchmoving enable? It recreates 3D points from our footage, so that we can reconstruct a 3D scene. This allows us to more accurately place our CG assets (props, vehicles, buildings or characters) within a reconstructed 3D scene.
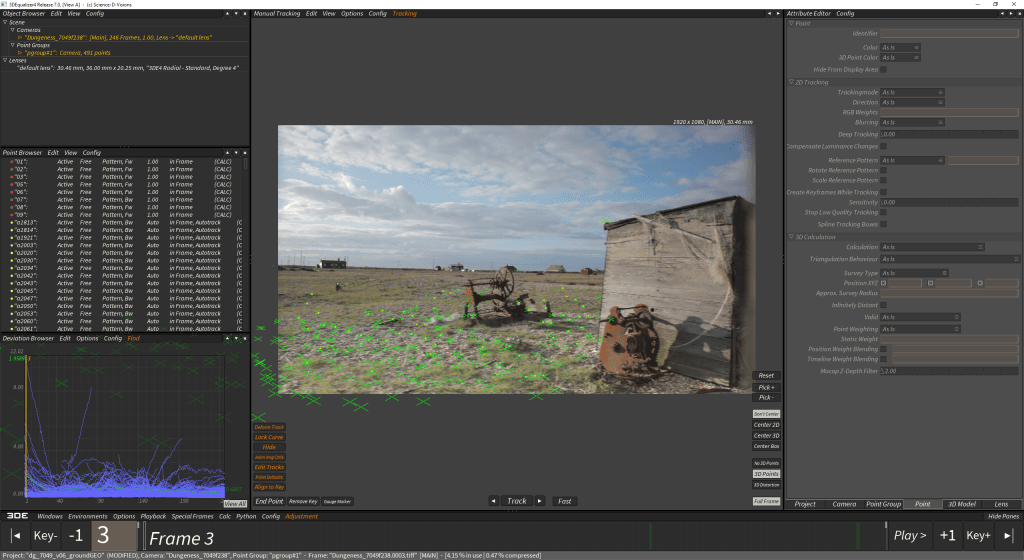
To start matchmoving we have to accurately track patterns/markers in our footage. The more accurately we do this will result in better data for the software algorithms to solve our matchmove. Once we have enough points spread through the shot, we can solve our camera and 3D points. We can also solve the focal length of the camera, which is important so that our 3D renders can look like they shot with the same lens as our original footage.
Lets look at the matchmoving process in 3dequalizer and Maya in the following video: Introduction to MatchMoving for Visual Effects. LINK to Vimeo password protected.
Carlos Poon – 3D VFX Tutor at Escape Studios